Steam turbine, Impulse and Reaction turbine working principle,Compounding of steam turbines
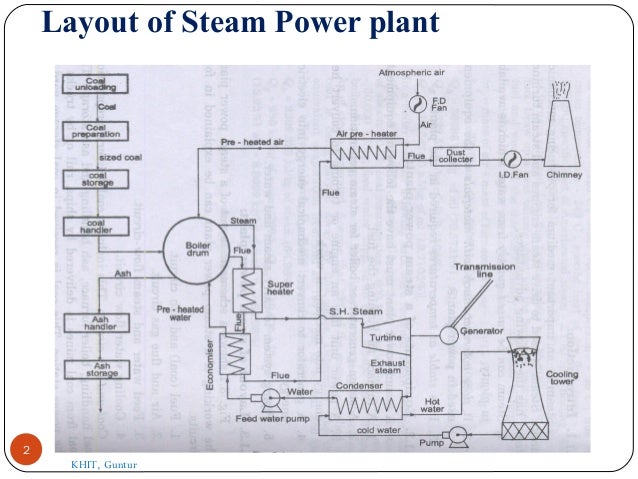













- 2. Layout of Steam Power plant 2 KHIT, Guntur
- 3. A steam turbine is a prime mover in which potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and then to Mechanical energy. Potential Energy Kinetic energy Mechanical Energy 3 KHIT, Guntur
- 4. Steam passage Boiler-Super heater- Economiser- Air pre heater-Turbine- Condenser Water flow Condenser-Feed water pump- Boiler KHIT,Guntur4
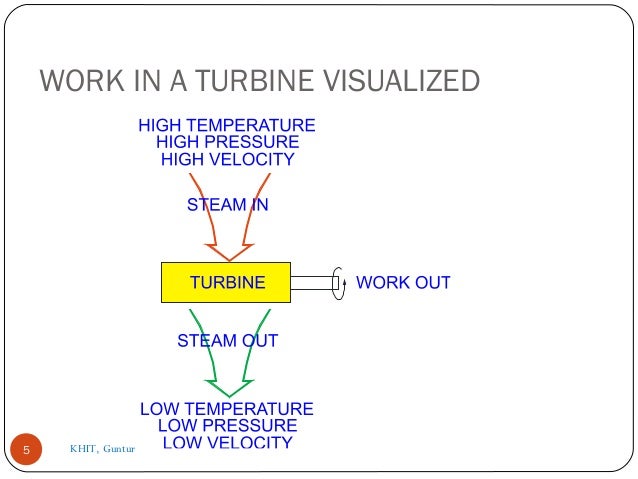
- 5. WORK IN A TURBINE VISUALIZED 5 KHIT, Guntur
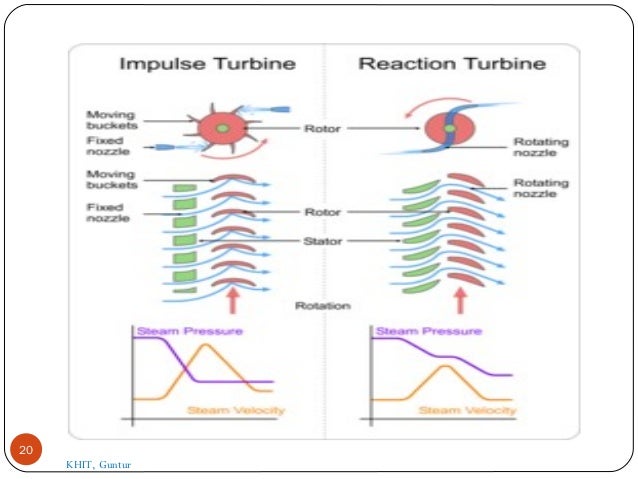
- 6. Description of common types of Turbines. 1. Impulse Turbine. 2. Reaction Turbine. The main difference between these two turbines lies in the way of expanding the steam while it moves through them. 6 KHIT, Guntur
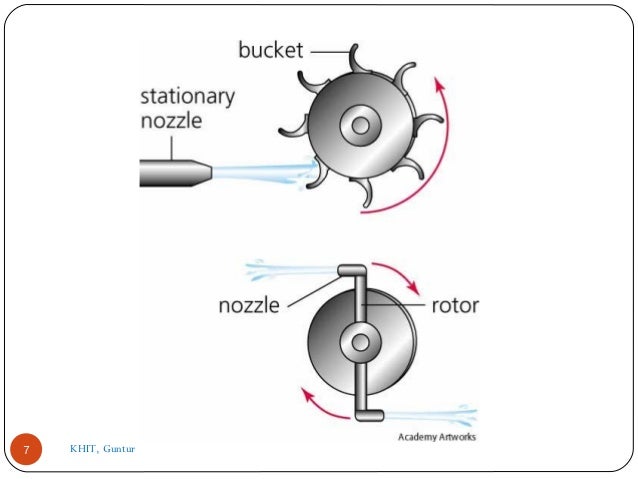
- 7. 7 KHIT, Guntur
- 8. In the impulse turbine, the steam expands in the nozzles and it's pressure does not alter as it moves over the blades. In the reaction turbine the steam expanded continuously as it passes over the blades and thus there is gradually fall in the pressure during expansion below the atmospheric pressure. 8
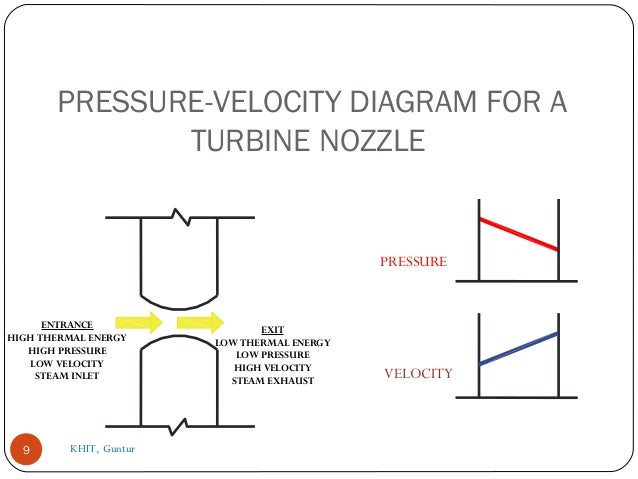
- 9. PRESSURE-VELOCITY DIAGRAM FOR A TURBINE NOZZLE 9 ENTRANCE HIGH THERMAL ENERGY HIGH PRESSURE LOW VELOCITY STEAM INLET EXIT LOW THERMAL ENERGY LOW PRESSURE HIGH VELOCITY STEAM EXHAUST PRESSURE VELOCITY KHIT, Guntur
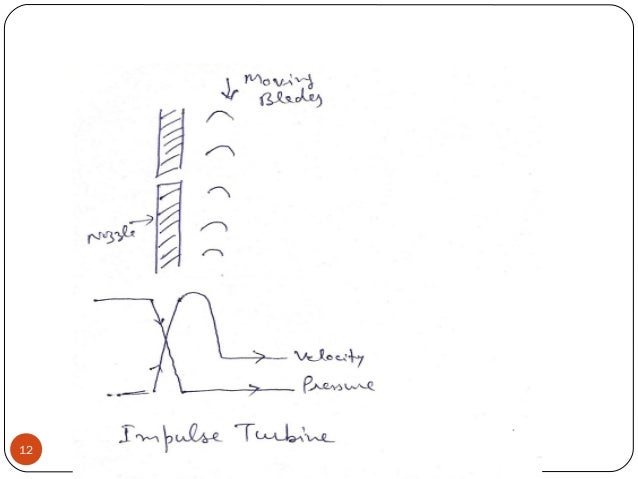
- 10. Simple impulse Turbine. It the impulse turbine, the steam expanded within the nozzle and there is no any change in the steam pressure as it passes over the blades 10 KHIT, Guntur
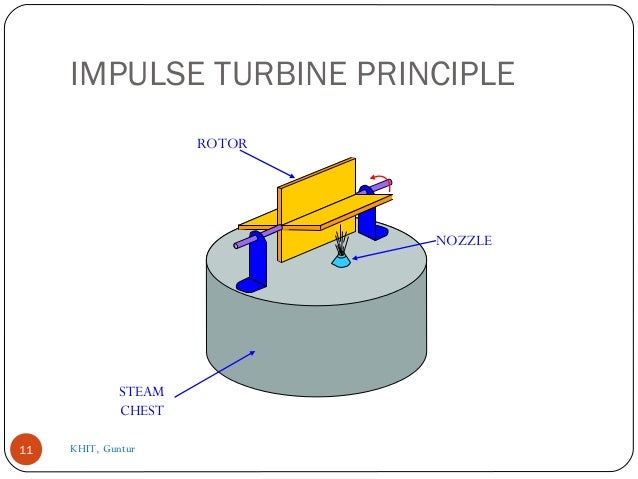
- 11. IMPULSE TURBINE PRINCIPLE 11 NOZZLE STEAM CHEST ROTOR KHIT, Guntur
- 12. 12
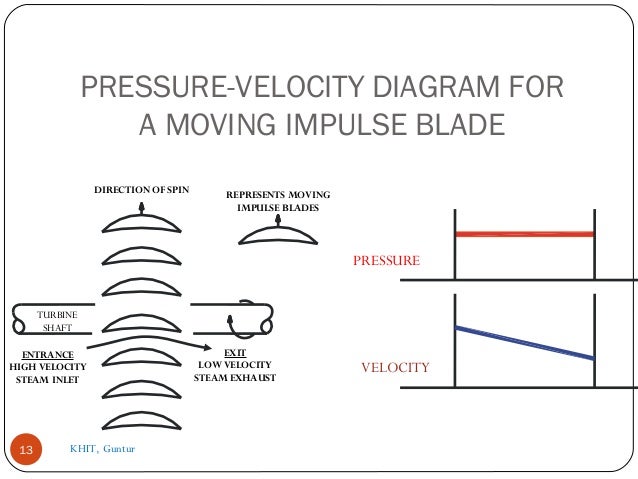
- 13. PRESSURE-VELOCITY DIAGRAM FOR A MOVING IMPULSE BLADE 13 VELOCITY PRESSURE TURBINE SHAFT DIRECTION OF SPIN ENTRANCE HIGH VELOCITY STEAM INLET REPRESENTS MOVING IMPULSE BLADES EXIT LOW VELOCITY STEAM EXHAUST KHIT, Guntur
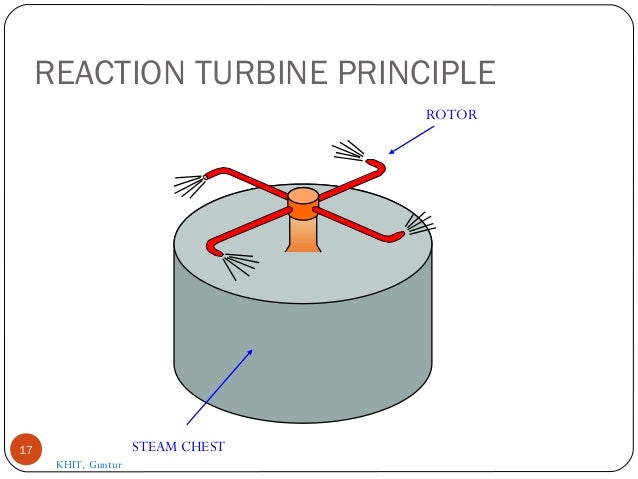
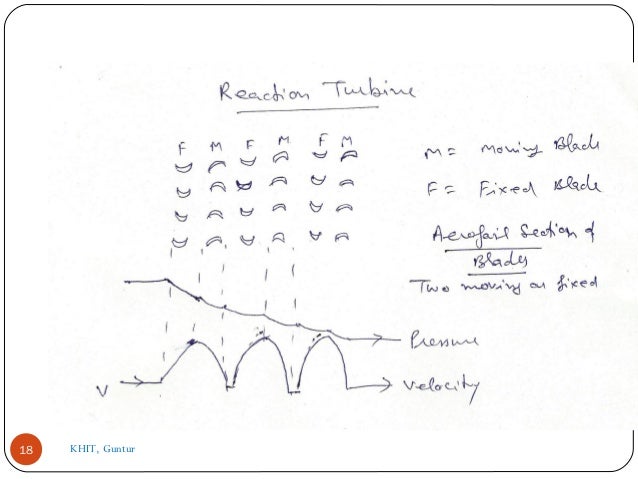
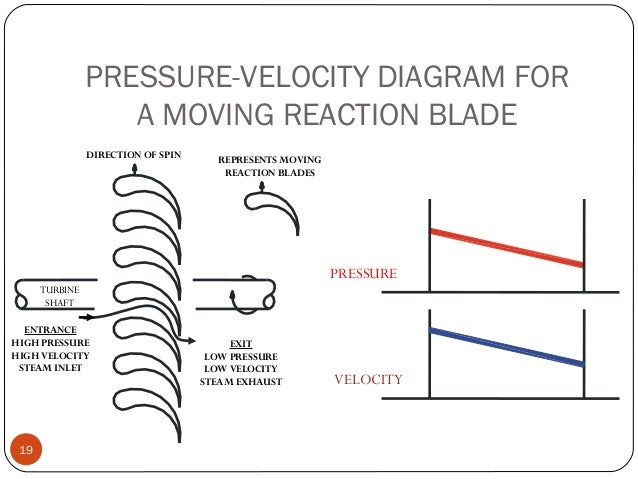
- 14. Reaction Turbine In this type of turbine, there is a gradual pressure drop and takes place continuously over the fixed and moving blades. The rotation of the shaft and drum, which carrying the blades is the result of both impulse and reactive force in the steam. The reaction turbine consist of a row of stationary blades and the following row of moving blades 14
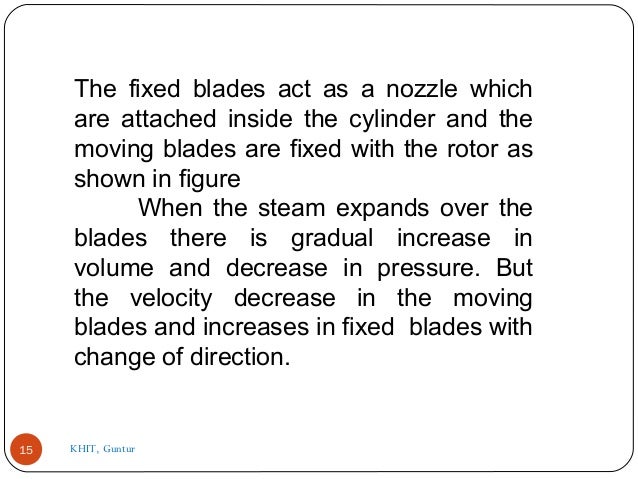
- 15. The fixed blades act as a nozzle which are attached inside the cylinder and the moving blades are fixed with the rotor as shown in figure When the steam expands over the blades there is gradual increase in volume and decrease in pressure. But the velocity decrease in the moving blades and increases in fixed blades with change of direction. 15 KHIT, Guntur
- 16. Because of the pressure drops in each stage, the number of stages required in a reaction turbine is much greater than in a impulse turbine of same capacity. It also concluded that as the volume of steam increases at lower pressures therefore the diameter of the turbine must increase after each group of blade rings. PES16
- 17. REACTION TURBINE PRINCIPLE 17 STEAM CHEST ROTOR KHIT, Guntur
- 18. 18 KHIT, Guntur
- 19. PRESSURE-VELOCITY DIAGRAM FOR A MOVING REACTION BLADE 19 TURBINE SHAFT DIRECTION OF SPIN ENTRANCE HIGH PRESSURE HIGH VELOCITY STEAM INLET REPRESENTS MOVING REACTION BLADES EXIT LOW PRESSURE LOW VELOCITY STEAM EXHAUST PRESSURE VELOCITY
- 20. 20 KHIT, Guntur
- 21. 21
- 22. .Compounding in Steam Turbine. The compounding is the way of reducing the wheel or rotor speed of the turbine to optimum value. Different methods of compounding are: 1.Velocity Compounding 2.Pressure Compounding 3.Pressure Velocity Compounding. In a Reaction turbine compounding can be achieved only by Pressure compounding.22 KHIT, Guntur
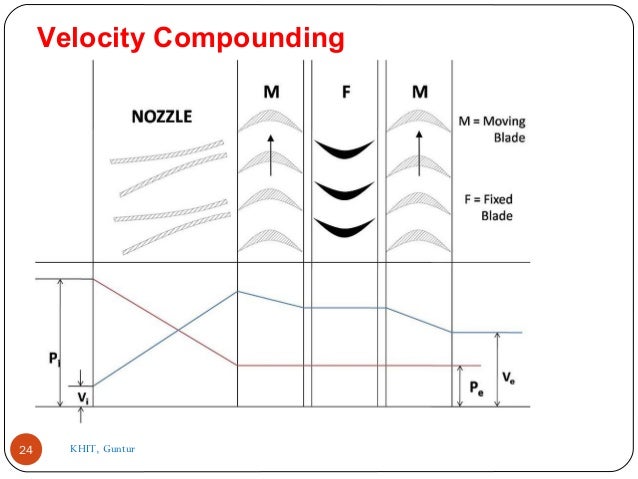
- 23. Velocity Compounding: There are number of moving blades separated by rings of fixed blades as shown in the figure. All the moving blades are keyed on a common shaft. When the steam passed through the nozzles where it is expanded to condenser pressure. It's Velocity becomes very high. This high velocity steam then passes through a series of moving and fixed blades. When the steam passes over the moving blades it's velocity decreases. The function of the fixed blades is to re-direct the steam flow without altering it's velocity to the following next row moving blades where a work is done on them and steam leaves the turbine with allow velocity as shown in diagram.23
- 24. 24 Velocity Compounding KHIT, Guntur
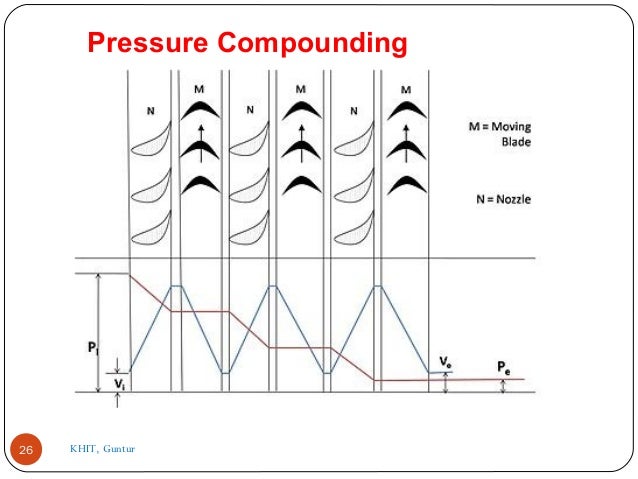
- 25. Pressure Compounding: These are the rings of moving blades which are keyed on a same shaft in series, are separated by the rings of fixed nozzles. The steam at boiler pressure enters the first set of nozzles and expanded partially. The kinetic energy of the steam thus obtained is absorbed by moving blades. The steam is then expanded partially in second set of nozzles where it's pressure again falls and the velocity increase the kinetic energy so obtained is absorbed by second ring of moving blades. 25
- 26. 26 Pressure Compounding KHIT, Guntur
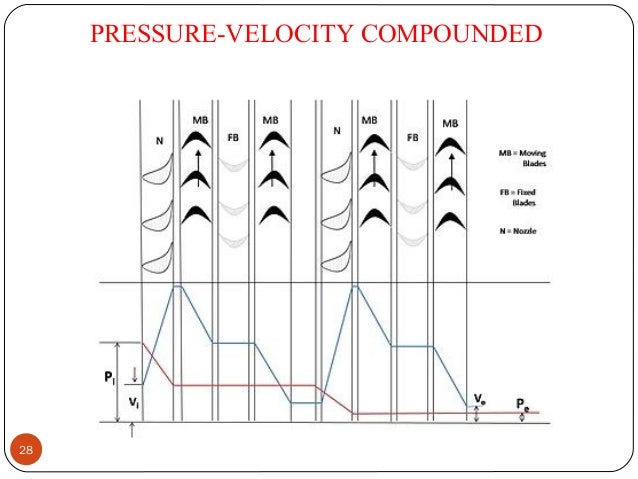
- 27. Pressure velocity compounding: This method of compounding is the combination of two previously discussed methods. The total drop in steam pressure is divided into stages and the velocity obtained in each stage is also compounded. The rings of nozzles are fixed at the beginning of each stage and pressure remains constant during each stage as shown in figure. The turbine employing this method of compounding may be said to combine many of the advantages of both pressure and velocity staging By allowing a bigger pressure drop in each stage, less number stages are necessary and hence a shorter turbine will be obtained for a given pressure drop. 27
- 28. PRESSURE-VELOCITY COMPOUNDED 28
- 29. 29 Reaction turbine pressure compounding KHIT, Guntur




























good work .
ReplyDelete